
A low coolant level will also cause your car to overheat, resulting in reduced engine performance and an illuminated Check Engine Light. Insufficient engine coolant and air pockets in your car’s cooling system can negatively affect the reading taken by the sensor.
This causes the sensor to malfunction and the Engine Control Unit to register an error code. The coolant temperature sensor terminals may get corroded due to water seepage. This can cause the ECM to generate a coolant sensor error code. The electrical connections to the coolant temperature sensor from the Engine Control Module (ECM) may get physically damaged from contact with the car’s moving parts, such as the transmission system. Listed below are the leading causes of coolant temperature sensor failure: 1. 3 Common Reasons a Coolant Temperature Sensor Goes Bad Now, let’s have a look at the possible reasons behind a faulty coolant temperature sensor. Incorrect information from the sensor can lead to transmission problems and reduced engine performance. The Transmission Control Module (TCM) uses the coolant temperature sensor reading to prevent the car from shifting into overdrive while the engine is cold. The opposite of this can also happen, resulting in the engine heating up beyond its operating temperature and getting damaged. Your car’s Engine Control Unit may turn on the radiator fan even when the engine isn’t hot enough due to a bad coolant sensor. Rough IdlingĪ malfunctioning ECT sensor may cause the Engine Control Unit to inject a fluctuating amount of fuel into the engine, resulting in rough idling. A faulty sensor can cause it to fluctuate erratically as you drive. The engine temperature gauge on your car’s dashboard gets its input from the coolant temperature sensor. A bad coolant temperature sensor may result in a lean fuel-air mixture, causing a difficult cold start. When you cold-start your car, the ECU calculates the required fuel-air mixture ratio by considering the coolant and ambient temperatures. A bad sensor may result in a rich fuel-air mixture, leading to black smoke from the exhaust pipe and poor fuel economy. Your car’s coolant temperature sensor helps its ECU decide the fuel-air mixture ratio for combustion.
#Chevy coolant temperature sensor symptoms code
It will also register an error code that can be read using an OBD-2 scan tool. Illuminated Check Engine LightĪ faulty sensor can result in the ECU activating the Check Engine Light on your car’s dashboard. The ECU will then adjust the fuel injection, ignition timing, and variable valve timing, further raising the engine’s temperature and causing it to overheat. Engine OverheatingĪ malfunctioning coolant temperature sensor may send an incorrect “cold” signal to the ECU, tricking it into believing the engine isn’t hot yet. Here are the key symptoms that accompany coolant temperature sensor failure: 1. 8 Signs of a Faulty Coolant Temperature Sensor Now let’s discuss the eight signs of a faulty sensor that can take a toll on your car’s engine performance. Your car’s cooling system may have multiple coolant temperature sensors, with the primary sensor located on the engine block near the thermostat housing or the radiator. The ECM detects a change in the voltage signal from the sensor and uses it to control: Your car’s coolant temperature sensor usually has a Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC), which means its resistance decreases with a rise in coolant temperature, resulting in a reduced voltage output signal. The ECM supplies the sensor with a constant reference voltage of 5V which the sensor converts into a suitable voltage signal according to the coolant temperature. It conveys this reading to the Engine Control Module (ECM), also referred to as the Engine Control Unit (ECU), which acts as the “brain” of your car. The coolant temperature sensor measures the temperature of the engine coolant through a resistor circuit.
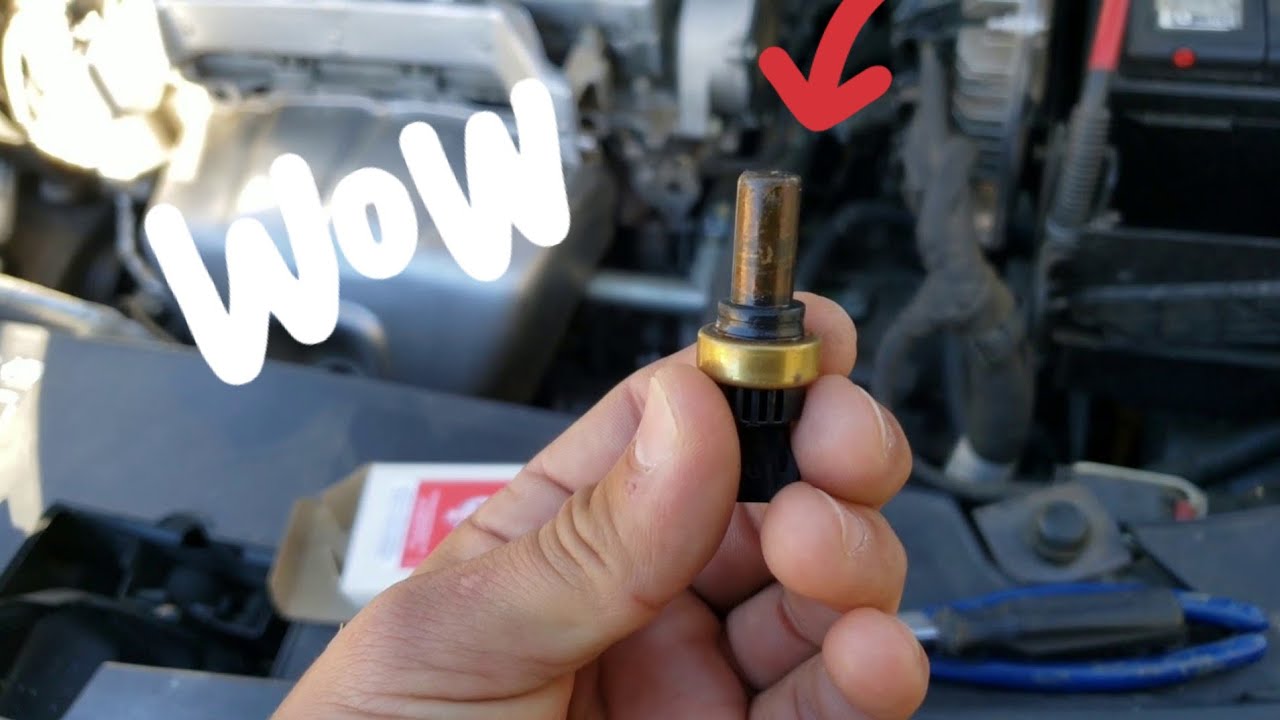


What Is an Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
